15 Enormous Spiders: Essential Guide To The World's Largest Arachnids

For those with a passion for the arachnid world, the allure of enormous spiders is hard to resist. These creatures, often shrouded in mystery and intrigue, captivate our imagination with their impressive size and unique characteristics. In this guide, we will delve into the fascinating realm of the world's largest spiders, uncovering their secrets and shedding light on their remarkable lives.
The Giants Among Us

The world of spiders is vast and diverse, but some species stand out for their exceptional size. Here, we present a list of 15 of the largest spiders known to roam the Earth:
Goliath Bird-eating Tarantula - Native to South America, this tarantula is renowned for its massive size, with leg spans reaching up to 30 cm. Its diet includes not only insects but also small birds, earning it its unique name.
Brazilian Salmon Pink Bird-eating Tarantula - Another South American giant, this tarantula boasts a stunning salmon-pink hue and a leg span of up to 25 cm. Despite its intimidating appearance, it is a popular pet among spider enthusiasts.
Giant Huntsman Spider - Found in Southeast Asia and Australia, this spider is known for its impressive speed and hunting abilities. With a leg span of up to 30 cm, it is one of the largest hunting spiders in the world.
Giant Tawny Red Tarantula - Native to Central and South America, this tarantula is a true giant, with a leg span of up to 25 cm. Its striking reddish-brown color and distinctive markings make it a favorite among collectors.
Camel Spider - Despite its intimidating name, the camel spider is not a true spider but a solifugid, a type of arachnid with a similar appearance. Found in desert regions, it can grow up to 15 cm in length and is known for its rapid movements.
Brazilian Whiteknee Tarantula - Hailing from Brazil, this tarantula is characterized by its striking white stripes on its legs. With a leg span of up to 20 cm, it is a popular choice for spider enthusiasts due to its docile nature.
Hickman's Roaming Spider - Endemic to Australia, this spider is a master of camouflage, blending seamlessly into its surroundings. It can grow up to 15 cm in length and is known for its wandering behavior.
Giant Cave Spider - As the name suggests, this spider is commonly found in caves and dark, humid environments. With a leg span of up to 20 cm, it is one of the largest cave-dwelling spiders in the world.
Black-footed Golden Orb-weaver - Native to Australia and Asia, this spider is renowned for its stunning golden web. Its body can reach up to 4 cm in length, and its leg span extends to approximately 15 cm.
Persian Peacock Spider - This tiny yet colorful spider is known for its intricate mating dance, which involves vibrant abdominal displays. Despite its small size, it captivates arachnophiles with its beauty.
Red-legged Golden Orb-weaver - Found in Australia and New Zealand, this spider is a skilled weaver, creating large, golden webs. With a body length of up to 4 cm and a leg span of around 12 cm, it is a common sight in gardens and forests.
Bird Dung Spider - As its name suggests, this spider resembles bird droppings, providing excellent camouflage. It can grow up to 10 cm in length and is commonly found in tropical regions.
Green Huntsman Spider - Native to Australia, this spider is known for its vibrant green coloration. With a leg span of up to 15 cm, it is a stunning addition to the arachnid world.
Giant Wood Spider - Found in the rainforests of South America, this spider is a true giant, with a leg span of up to 30 cm. Its diet consists mainly of insects and small vertebrates.
Giant Crab Spider - This spider gets its name from its distinctive crab-like appearance and powerful front legs. It can grow up to 10 cm in length and is commonly found in gardens and forests.
Atlas Desert Spider - Native to North Africa and the Middle East, this spider is well-adapted to desert environments. With a leg span of up to 15 cm, it is one of the largest desert-dwelling spiders.
Characteristics and Behaviors

Enormous spiders exhibit a range of fascinating characteristics and behaviors that set them apart from their smaller counterparts. Here are some key aspects to explore:
Size and Physical Attributes

The most striking feature of these spiders is, of course, their size. With leg spans ranging from 10 cm to over 30 cm, they command attention and often inspire awe (or fear) in those who encounter them. Their size allows them to hunt larger prey and establish dominance in their respective habitats.
Diet and Hunting Strategies
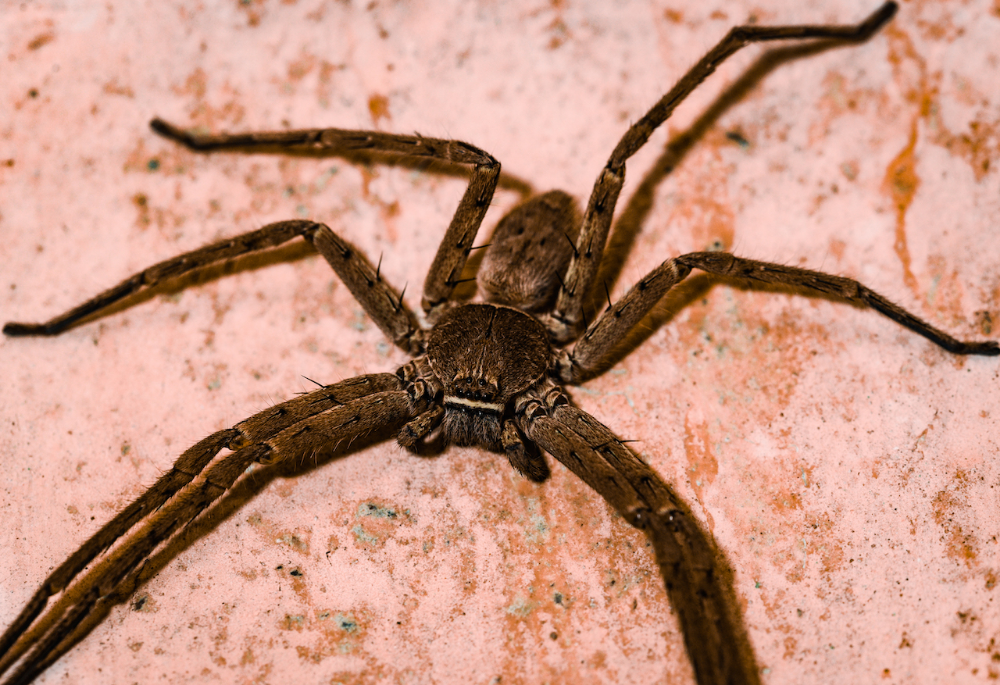

The diet of these spiders varies, but many are opportunistic hunters. Some, like the Goliath Bird-eating Tarantula, are known to consume small birds and mammals, while others, such as the Giant Huntsman Spider, prefer insects and other arthropods. Their hunting strategies can range from ambushing prey to actively pursuing it with incredible speed and agility.
Web-Building Abilities
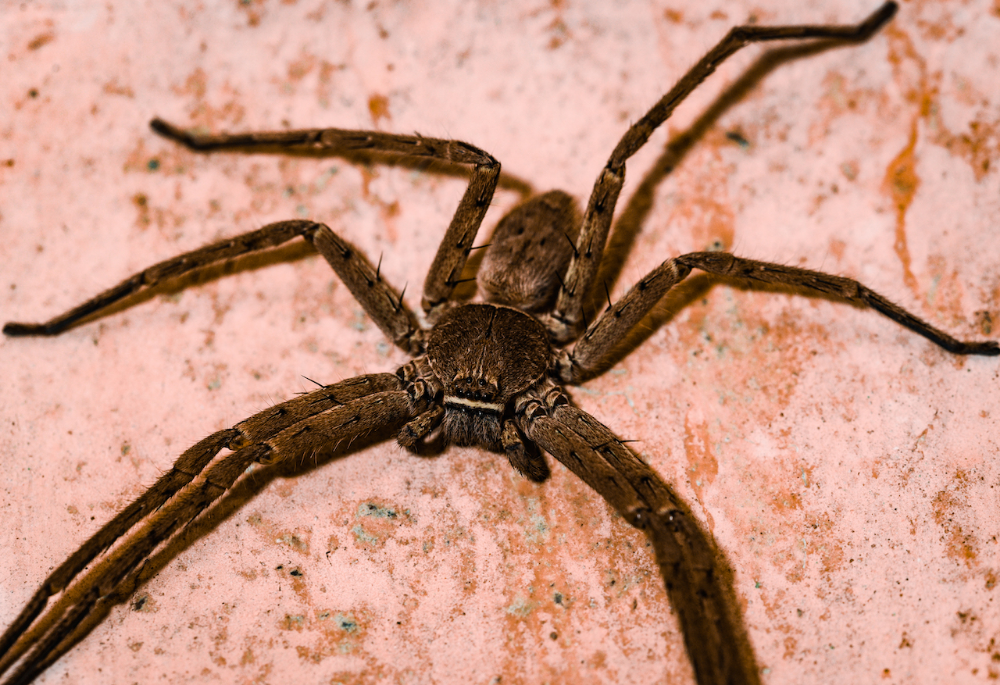

While not all enormous spiders build webs, those that do are truly remarkable. The Golden Orb-weavers, for example, create intricate and sturdy webs that can trap even the largest of insects. These webs are often adorned with silk decorations, adding to their beauty and functionality.
Defense Mechanisms

When it comes to defense, these spiders have evolved a range of strategies. Some, like the Brazilian Salmon Pink Bird-eating Tarantula, rely on their formidable fangs and venomous bite to deter predators. Others, such as the Giant Wood Spider, use their size and aggressive behavior to ward off potential threats.
Reproduction and Life Cycle

The reproductive behaviors of enormous spiders are just as fascinating. Many species engage in elaborate courtship rituals, with males performing intricate dances or presenting nuptial gifts to attract females. After mating, females often construct silk egg sacs to protect their offspring, ensuring the survival of the next generation.
Habitat and Distribution

The world's largest spiders are found in a variety of habitats, from tropical rainforests to arid deserts. Here is a glimpse into their preferred environments:
Tropical Rainforests
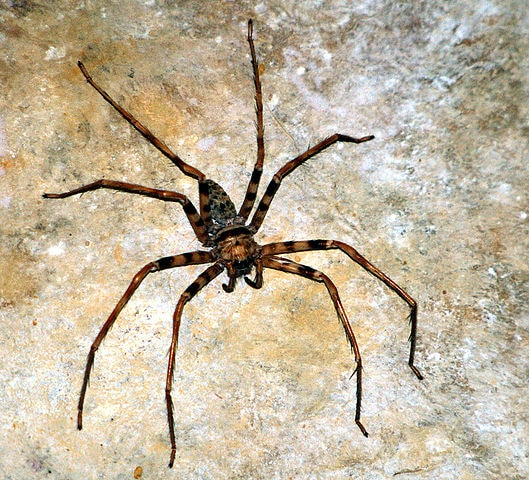

Many enormous spiders, such as the Goliath Bird-eating Tarantula and the Giant Wood Spider, call tropical rainforests their home. These lush environments provide an abundance of prey and shelter, allowing these spiders to thrive.
Deserts and Arid Regions
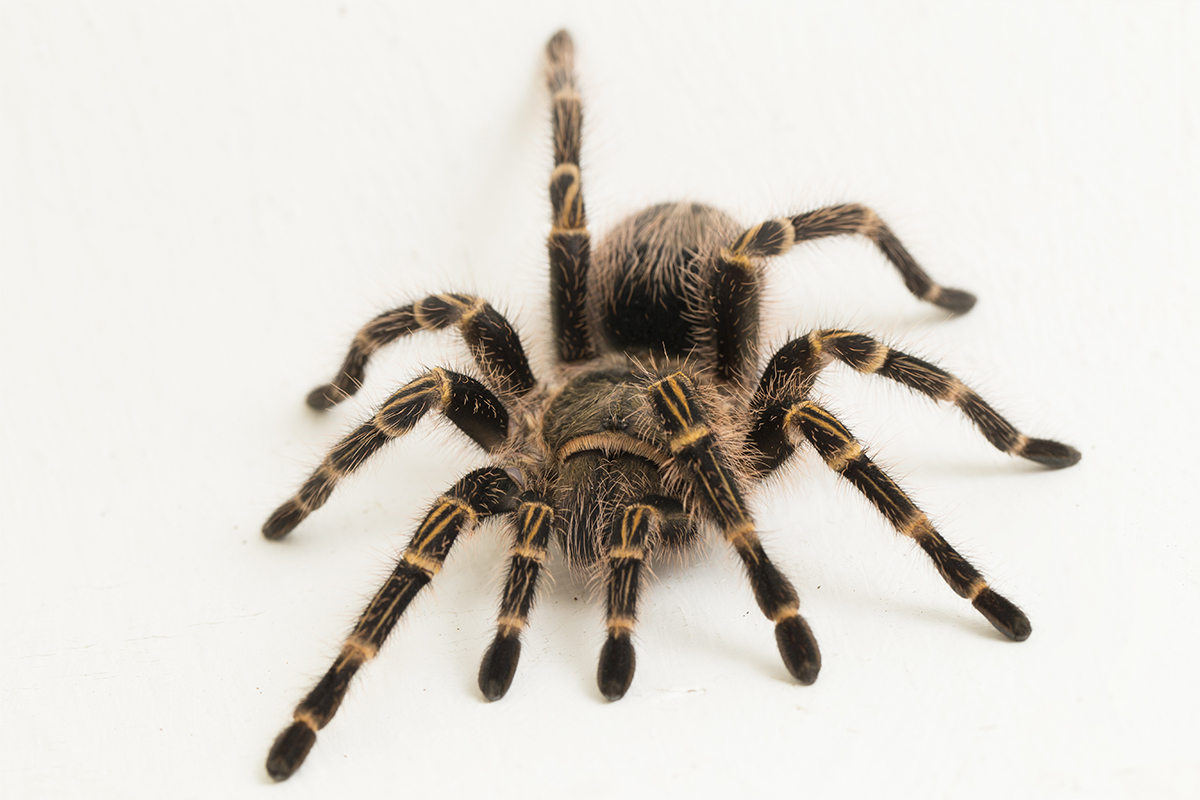

Spiders like the Camel Spider and the Atlas Desert Spider have adapted to survive in harsh desert conditions. They are well-equipped to handle extreme temperatures and limited water sources, making them true survivors in these challenging environments.
Caves and Dark Environments

The Giant Cave Spider, as its name suggests, is commonly found in caves and other dark, humid places. These spiders have evolved to thrive in low-light conditions, using their keen senses to navigate and hunt in these unique habitats.
Gardens and Forests

Some enormous spiders, such as the Red-legged Golden Orb-weaver, are commonly encountered in gardens and forests. These spiders play a crucial role in controlling insect populations and maintaining the balance of their ecosystems.
Conservation and Threats

Despite their impressive size and unique characteristics, many of the world's largest spiders face threats to their survival. Habitat destruction, pollution, and the illegal pet trade are among the challenges they encounter. It is crucial to raise awareness and promote conservation efforts to ensure the long-term survival of these remarkable creatures.
Key Threats and Conservation Efforts

Habitat loss due to deforestation and urban development poses a significant threat to many spider species. Protecting their natural habitats and implementing sustainable land-use practices is essential for their conservation. Additionally, raising awareness about the importance of spiders in ecosystems and dispelling misconceptions can help reduce negative attitudes towards these arachnids.
Educational Initiatives
Educating the public about the fascinating world of spiders and their ecological significance is crucial. By fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation for these creatures, we can encourage responsible behavior and support conservation initiatives. Educational programs, nature documentaries, and interactive exhibits can play a vital role in engaging and inspiring individuals to become advocates for spider conservation.
Research and Monitoring
Conducting research on the biology, behavior, and distribution of enormous spiders is essential for effective conservation planning. Scientists and researchers play a crucial role in gathering data, studying their ecological roles, and identifying potential threats. By monitoring populations and tracking their movements, we can better understand the needs of these spiders and develop targeted conservation strategies.
Interacting with Enormous Spiders

For those fascinated by these arachnids, interacting with enormous spiders can be a thrilling experience. However, it is essential to approach them with respect and caution. Here are some guidelines for safe and responsible interactions:
Observing in the Wild
If you encounter an enormous spider in its natural habitat, maintain a safe distance and avoid disturbing it. Use binoculars or a telephoto lens to observe its behavior without causing stress or harm. Remember, these spiders play vital roles in their ecosystems, and it is important to respect their space.
Spider Keeping as Pets
For arachnophiles who wish to keep enormous spiders as pets, it is crucial to do thorough research and ensure you have the necessary knowledge and resources. Providing a suitable enclosure, proper diet, and adequate care is essential for the well-being of these spiders. Always prioritize the spider's needs and consult with experts to ensure you can provide the best possible environment.
Handling and Safety Precautions
When handling enormous spiders, always prioritize your safety and the well-being of the spider. Wear protective gear, such as gloves and long sleeves, to minimize the risk of accidental bites. Handle them gently and avoid sudden movements that may startle or provoke them. Remember, even the most docile spiders can become defensive if they feel threatened.
Conclusion
The world of enormous spiders is a fascinating and diverse realm, filled with incredible creatures that challenge our perceptions. From their impressive size and unique characteristics to their vital roles in ecosystems, these spiders deserve our admiration and protection. By learning about their behaviors, habitats, and conservation needs, we can become advocates for their survival and ensure that future generations can continue to marvel at these magnificent arachnids.
How large can the Goliath Bird-eating Tarantula grow?
+The Goliath Bird-eating Tarantula can reach an impressive leg span of up to 30 cm, making it one of the largest spiders in the world.
Are enormous spiders dangerous to humans?
+While some enormous spiders, such as tarantulas, can deliver a painful bite, they are generally not considered dangerous to humans. Most species are shy and will only bite if provoked or threatened.
Can I keep an enormous spider as a pet?
+Yes, many species of enormous spiders, such as tarantulas, are kept as pets by arachnid enthusiasts. However, it is crucial to research and ensure you can provide the proper care and environment for their well-being.
What is the role of enormous spiders in ecosystems?
+Enormous spiders play a crucial role in controlling insect populations and maintaining the balance of their ecosystems. They are top predators, helping to regulate the numbers of smaller arthropods and contributing to the overall health of their habitats.
How can I support spider conservation efforts?
+You can support spider conservation by raising awareness, educating others about the importance of spiders, and supporting organizations dedicated to their protection. Additionally, minimizing habitat destruction and reducing the use of pesticides can have a positive impact on spider populations.


